Qt Android Activity View
May 23, 2022 by Ramon Sadornil Rivera | Comments
Qt for Android Automotive creates a bridge between the world of Qt and the Android Automotive environment. It provides excellent flexibility in terms of accessing car data. Depending on the needs, you can use tools for automatic code generation based on a high-level description or ready-to-use QML components.
The Qt Android ActivityView module has been added to Qt for Android Automotive in version 6.3.0. Currently, Android 10 and 11 are supported.
When it comes to UI, all the benefits provided by Qt are available. The natural choice is to use QML and Qt Design Studio to create a modern graphical interface quickly and efficiently.
Often, however, there is a need to leverage existing Android applications - directly or after adaptation to specific requirements. An integrated home screen composed of selected embedded applications could be an example. The new Activity View module provides a component that allows embedding external Android applications into the Qt-based one. The feature is as easy to use as any other visual QML component, including support for Qt Design Studio.
The primary use case is as simple as the QML code below. You can position the component using anchors. Additionally, a busy indicator is displayed while the external application is loading:
import QtQuick
import QtQuick.Controls
import QtAndroidAutomotive.ActivityView
ApplicationWindow {
visible: true
BusyIndicator {
anchors.centerIn: parent
visible: activityView.status !== ActivityView.Started
}
ActivityView {
id: activityView
anchors.centerIn: parent
width: 600
height: 800
radius: 25
packageName: "com.google.earth"
}
}
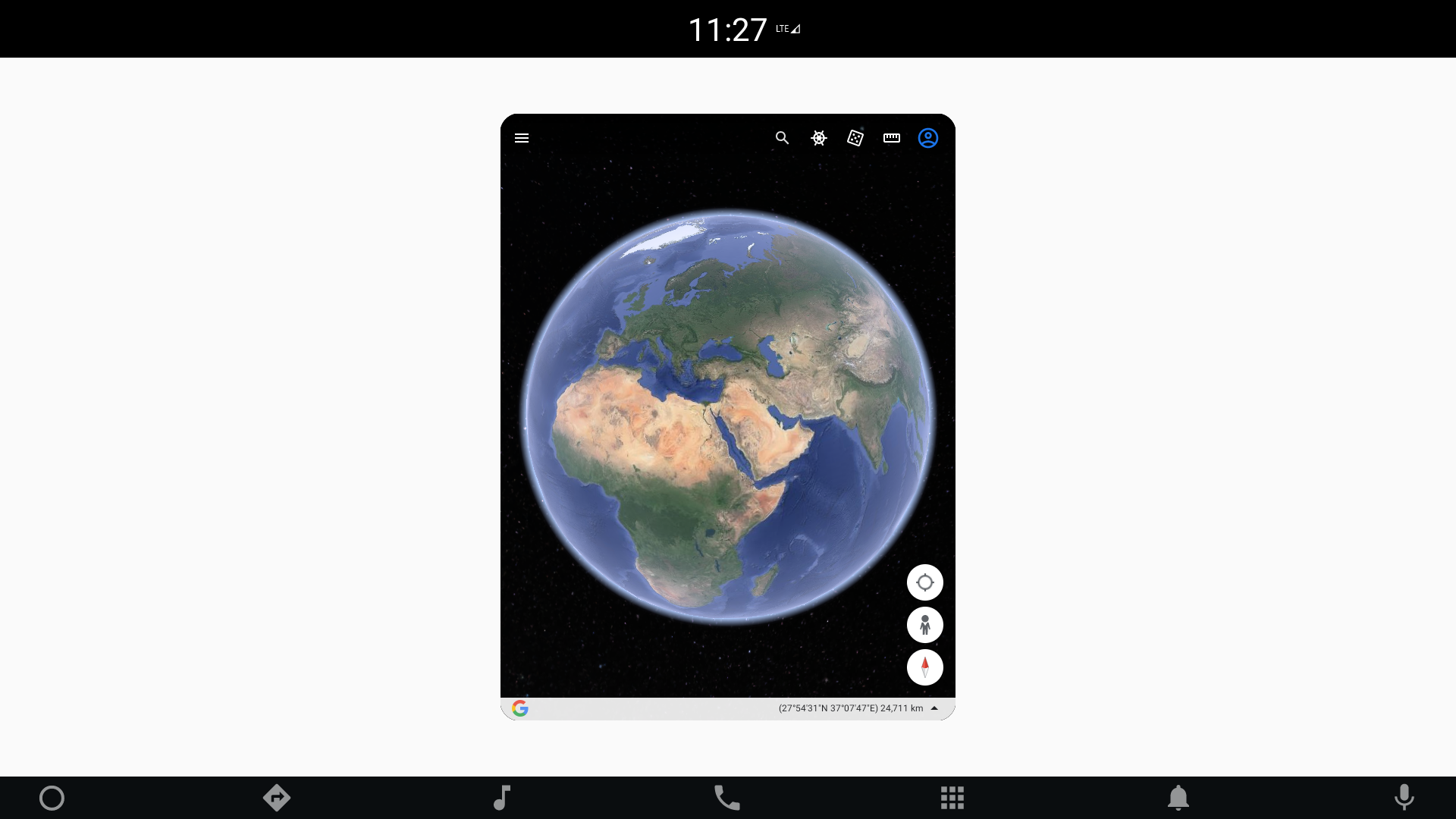
Of course, you can also use ActivityView with layout components. The snippet below launches two applications positioned using a row layout:
import QtQuick
import QtQuick.Controls
import QtQuick.Layouts
import QtAndroidAutomotive.ActivityView
ApplicationWindow {
visible: true
RowLayout {
anchors.fill: parent
anchors.margins: 25
spacing: 25
ActivityView {
Layout.fillWidth: true
Layout.fillHeight: true
radius: 25
packageName: "com.google.earth"
}
ActivityView {
Layout.fillWidth: true
Layout.fillHeight: true
radius: 25
packageName: "com.android.deskclock"
}
}
}
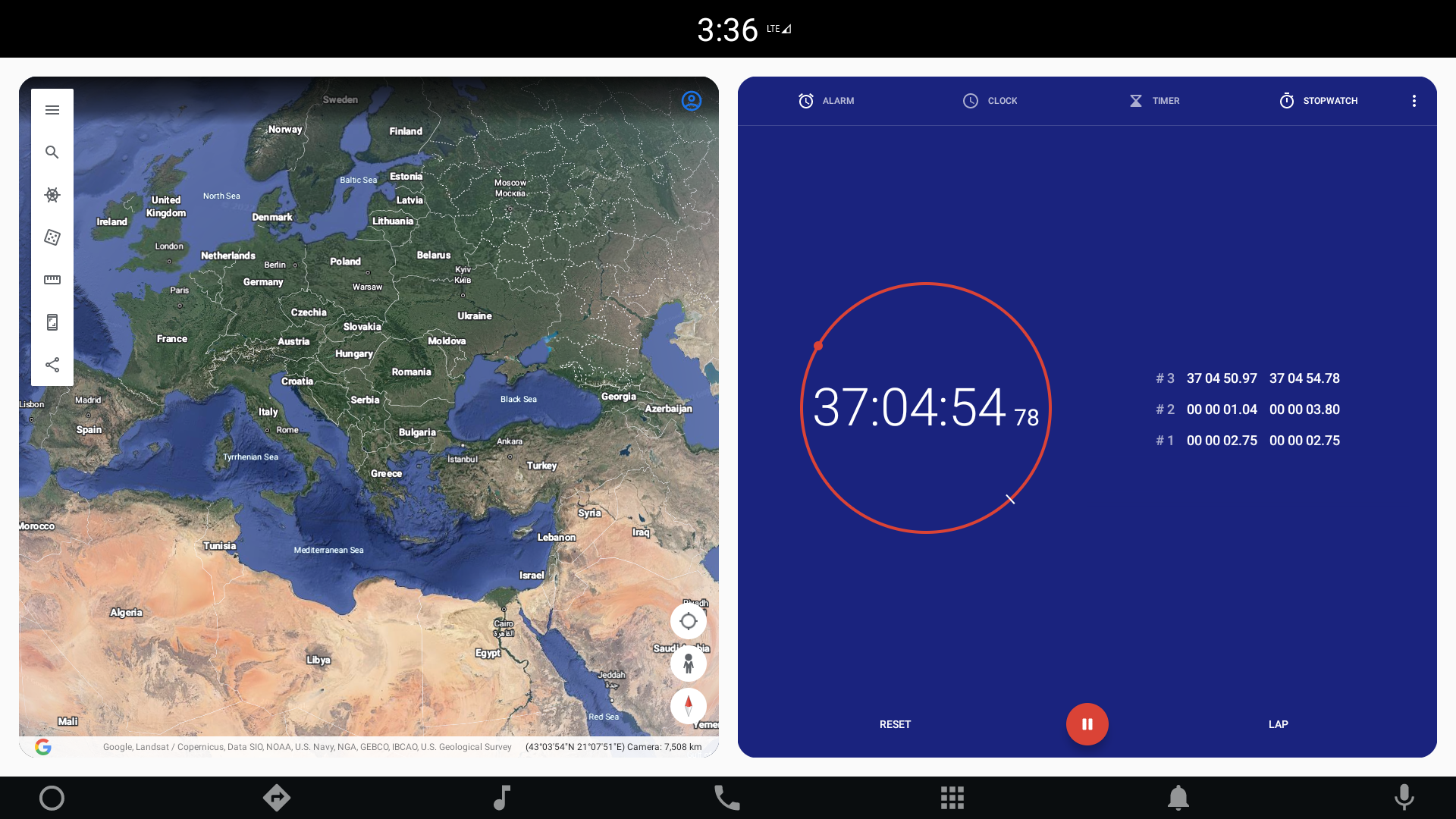
You can also manipulate the component size and position dynamically. One of the examples provided with the module presents external applications wrapped in windows created in QML. Changing the location and size of an external application is a heavy operation. Therefore, the component allows you to define a placeholder that will be displayed, instead of the actual application, during these operations: 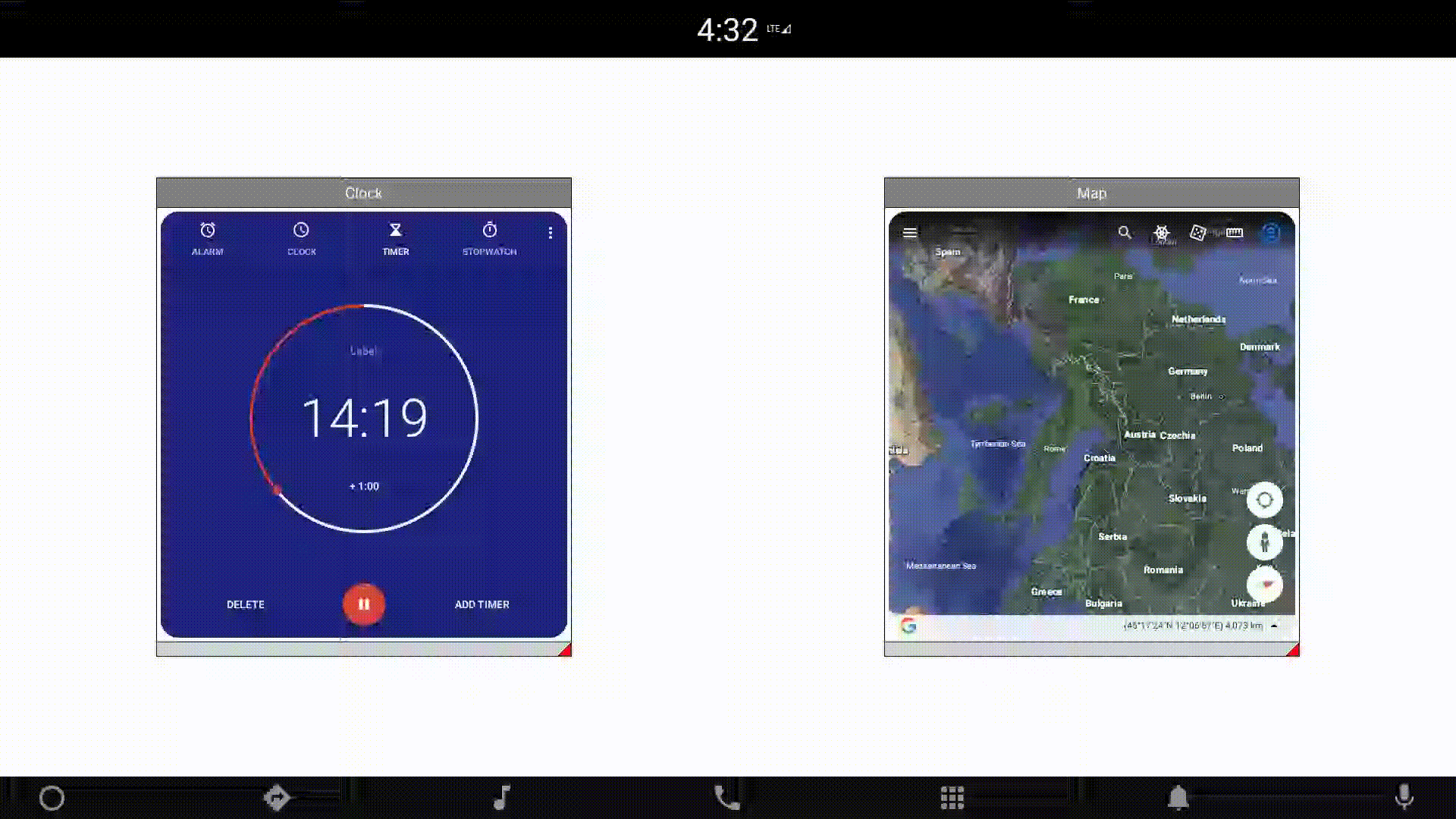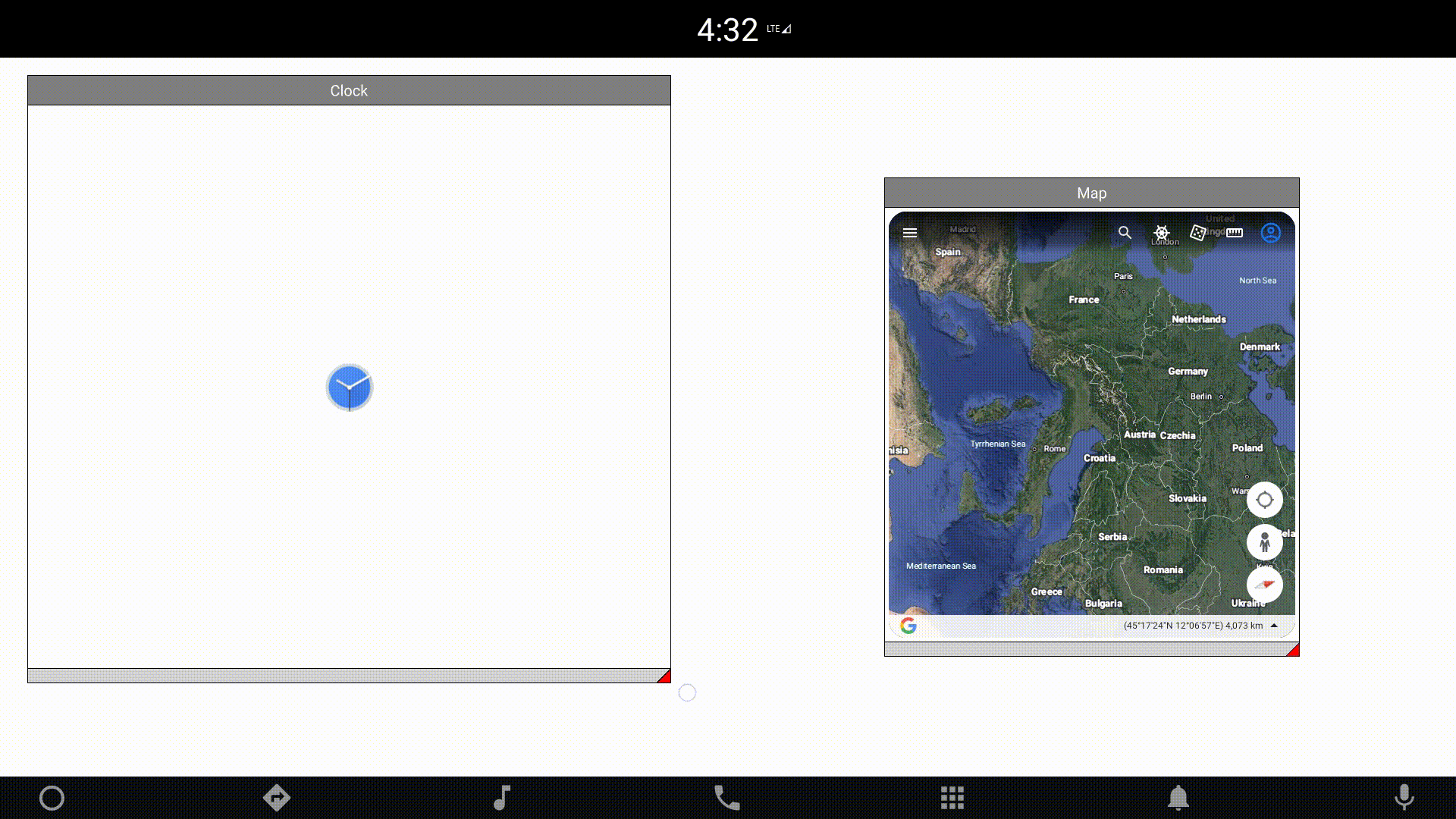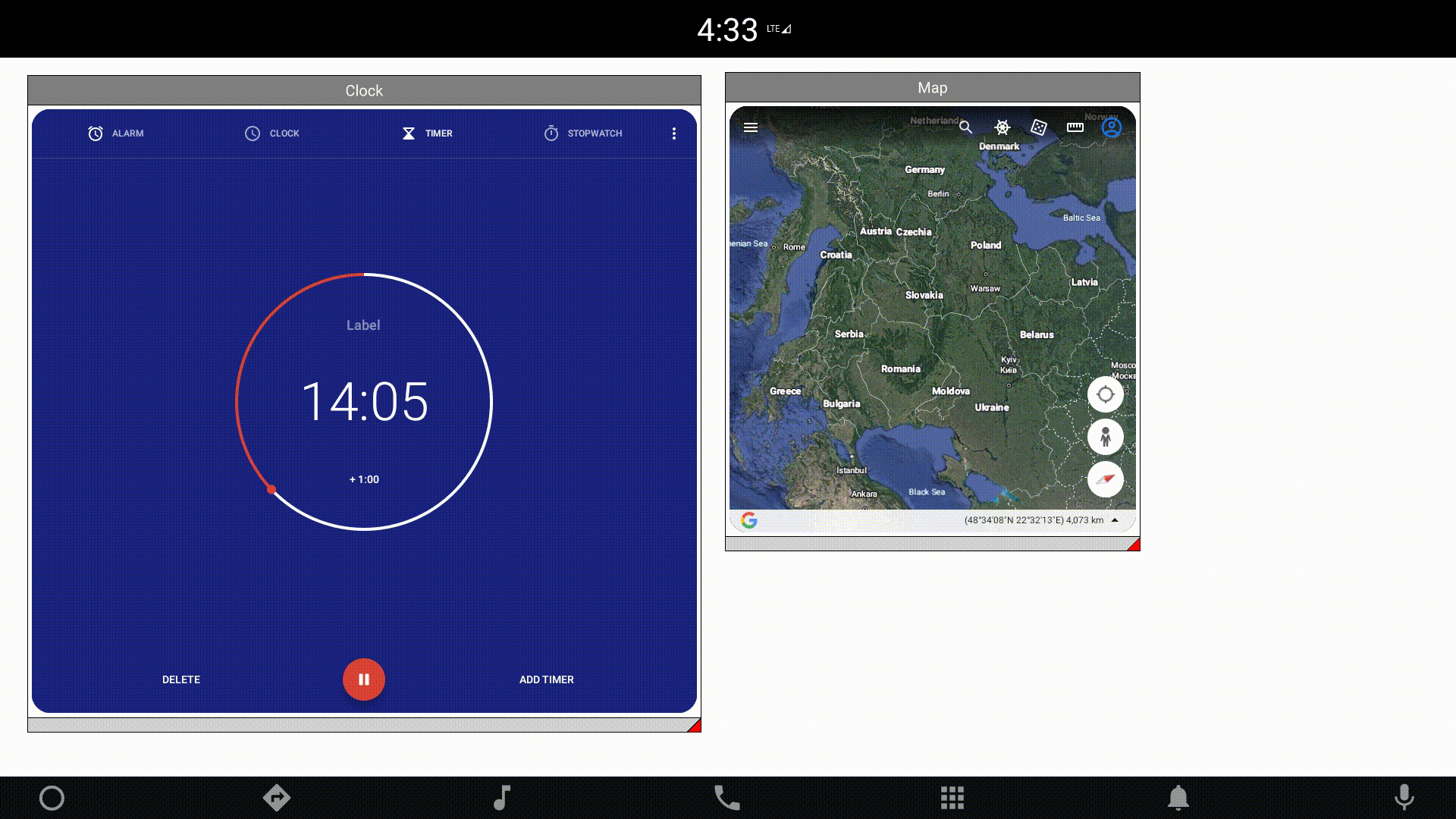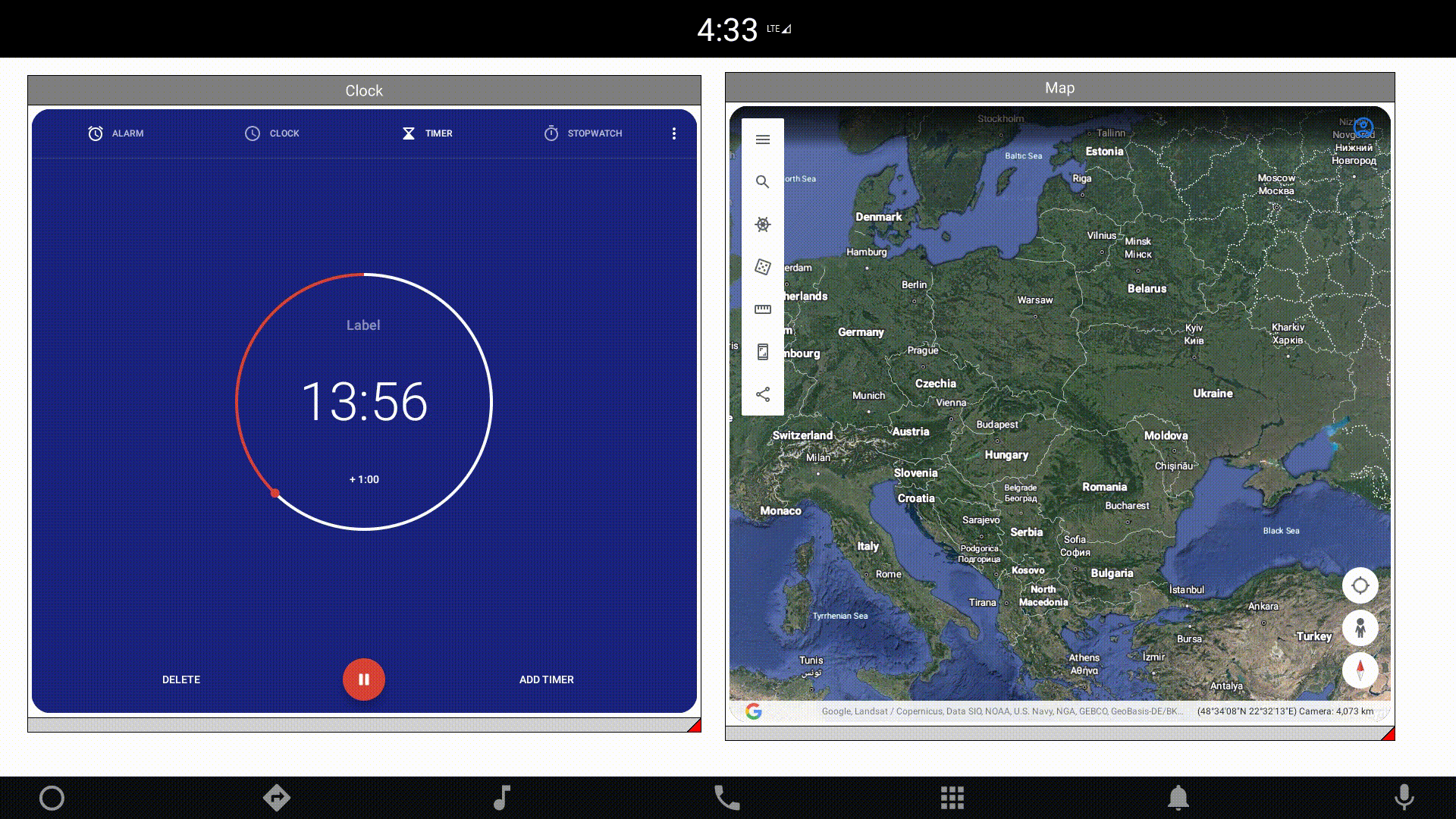
In addition to the QML component, the Activity View module also provides a C++ API offering the same capabilities without dependence on QML.
Note, however, that Activity View is not a standard visual QML component managed by a scene graph. This implies some limitations. Every Activity View component is always rendered above the QML scene. It is also impossible to intercept events from the element, e.g., with the MouseArea.
You can find more details about the new module in the documentation: Qt Android Activity View.
Blog Topics:
Comments
Subscribe to our newsletter
Subscribe Newsletter
Try Qt 6.9 Now!
Download the latest release here: www.qt.io/download.
Qt 6.9 is now available, with new features and improvements for application developers and device creators.
We're Hiring
Check out all our open positions here and follow us on Instagram to see what it's like to be #QtPeople.



Commenting for this post has ended.